Cookbook: Observability for OpenAI Assistants API with Langfuse
This cookbook demonstrates how to use the Langfuse observe decorator to trace calls made to the OpenAI Assistants API. It covers creating an assistant, running it on a thread, and observing the execution with Langfuse tracing.
Note: The native OpenAI SDK wrapper does not support tracing of the OpenAI assistants API, you need to instrument it via the decorator as shown in this notebook.
What is the Assistants API?
The Assistants API from OpenAI allows developers to build AI assistants that can utilize multiple tools and data sources in parallel, such as code interpreters, file search, and custom tools created by calling functions. These assistants can access OpenAI’s language models like GPT-4 with specific prompts, maintain persistent conversation histories, and process various file formats like text, images, and spreadsheets. Developers can fine-tune the language models on their own data and control aspects like output randomness. The API provides a framework for creating AI applications that combine language understanding with external tools and data.
Example Trace Output
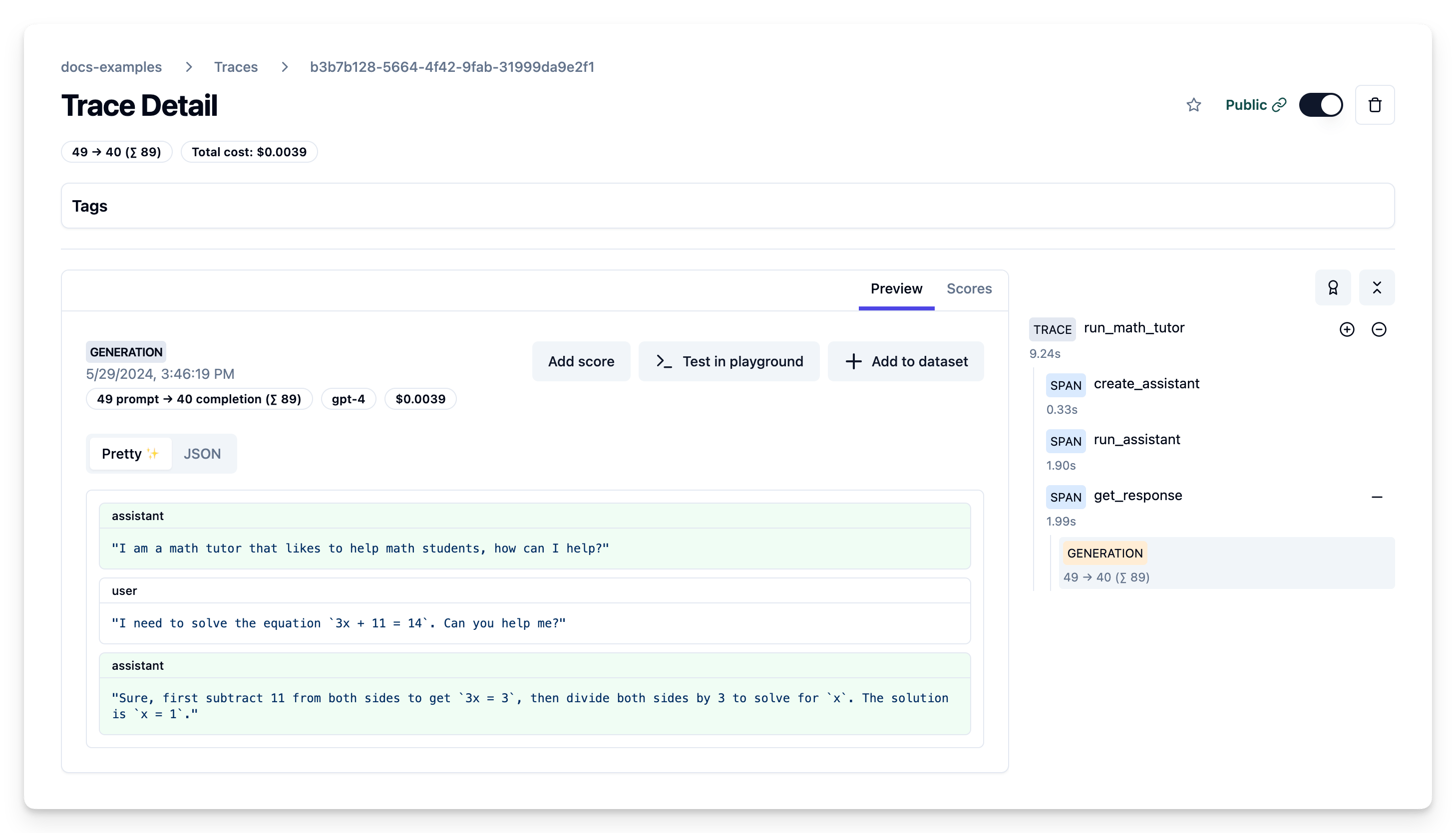
Setup
Install the required packages:
%pip install --upgrade openai langfuseSet your environment:
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page
# https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""Step by step
1. Creating an Assistant
Use the client.beta.assistants.create method to create a new assistant. Alternatively you can also create the assistant via the OpenAI console:
from langfuse.decorators import observe
from openai import OpenAI
@observe()
def create_assistant():
client = OpenAI()
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="Math Tutor",
instructions="You are a personal math tutor. Answer questions briefly, in a sentence or less.",
model="gpt-4"
)
return assistant
assistant = create_assistant()
print(f"Created assistant: {assistant.id}")Public link of example trace of assistant creation
2. Running the Assistant
Create a thread and run the assistant on it:
@observe()
def run_assistant(assistant_id, user_input):
client = OpenAI()
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id, role="assistant", content="I am a math tutor that likes to help math students, how can I help?"
)
client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id, role="user", content=user_input
)
run = client.beta.threads.runs.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant_id,
)
return run, thread
user_input = "I need to solve the equation `3x + 11 = 14`. Can you help me?"
run, thread = run_assistant(assistant.id, user_input)
print(f"Created run: {run.id}")Public link of example trace of message and trace creation
3. Getting the Response
Retrieve the assistant’s response from the thread:
import json
from langfuse.decorators import langfuse_context
@observe()
def get_response(thread_id, run_id):
client = OpenAI()
messages = client.beta.threads.messages.list(thread_id=thread_id, order="asc")
assistant_response = messages.data[-1].content[0].text.value
# get run for token counts
run_log = client.beta.threads.runs.retrieve(
thread_id=thread_id,
run_id=run_id
)
message_log = client.beta.threads.messages.list(
thread_id=thread_id,
)
input_messages = [{"role": message.role, "content": message.content[0].text.value} for message in message_log.data[::-1][:-1]]
# log internal generation within the openai assistant as a separate child generation to langfuse
# get langfuse client used by the decorator, uses the low-level Python SDK
langfuse_client = langfuse_context.client_instance
# pass trace_id and current observation ids to the newly created child generation
langfuse_client.generation(
trace_id=langfuse_context.get_current_trace_id(),
parent_observation_id=langfuse_context.get_current_observation_id(),
model=run.model,
usage_details=run.usage,
input=input_messages,
output=assistant_response
)
return assistant_response, run
response = get_response(thread.id, run.id)
print(f"Assistant response: {response[0]}")Public link of example trace of fetching the response
All in one trace
import time
@observe()
def run_math_tutor(user_input):
assistant = create_assistant()
run, thread = run_assistant(assistant.id, user_input)
time.sleep(5) # notebook only, wait for the assistant to finish
response = get_response(thread.id, run.id)
return response[0]
user_input = "I need to solve the equation `3x + 11 = 14`. Can you help me?"
response = run_math_tutor(user_input)
print(f"Assistant response: {response}")The Langfuse trace shows the flow of creating the assistant, running it on a thread with user input, and retrieving the response, along with the captured input/output data.

Learn more
If you use non-Assistants API endpoints, you can use the OpenAI SDK wrapper for tracing. Check out the Langfuse documentation for more details.